Client overview
Chip Inc is building an AI powered research assistant for academics. The goal is simple to state and hard to ship: help researchers move faster by automating the tedious parts of research while still supporting serious computation and reproducible workflows.
The problem
Academic research has a hidden tax that steals time from actual thinking.
- Manual data work eats hours: gathering sources, cleaning data, extracting tables, rewriting code, rerunning experiments.
- Computation is fragmented: researchers bounce between Python, MATLAB, symbolic tools, notebooks, and web tools, often with painful setup and dependency issues.
- Tools lack project memory: most assistants answer a question, then forget the project context and assumptions that make research coherent.
- Safety and control matter: autonomous actions such as credentials, external tools, and code execution need guardrails, not blind automation.
Goals
- Build an AI research bot tailored for academic workflows, not generic chat.
- Enable real execution, including advanced interpreters and symbolic math tooling.
- Support end to end research pipelines: retrieval, computation, drafting, and iteration.
- Keep the system modular so new tools and workflows can be added without rewriting the core.
The solution
Krazimo partnered with Chip Inc to build a modular “research executor” that combines:
- A conversational interface for research queries and planning
- A multi agent orchestration layer for retrieval, memory, reasoning, and verification
- A controlled execution environment for running code, math tools, and workflows
- A browser automation subsystem for parallel research and action steps
- A security and interruption framework so autonomy remains user controlled
In other words, it is not a chatbot. It is a research assistant that can retrieve, run, verify, and iterate.
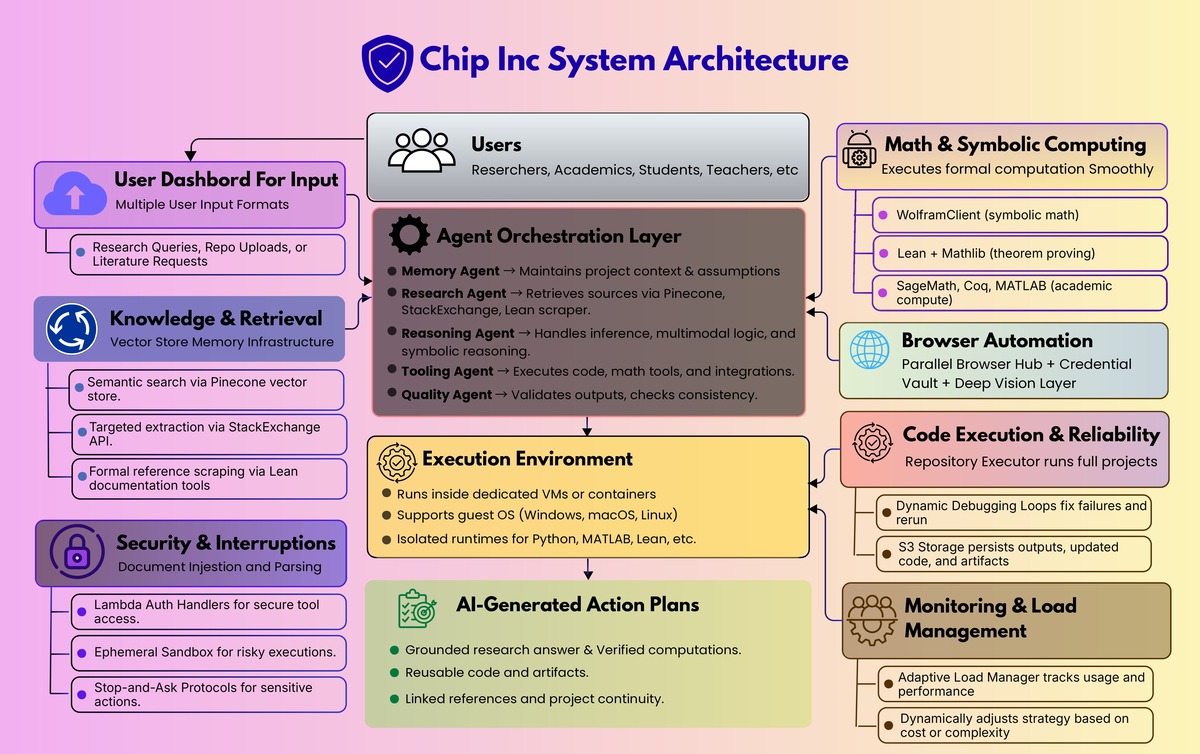
Architecture overview
1) Core agent orchestration
At the center is an orchestrator that plans work, delegates to specialists, and compiles the final output:
- Orchestrator Agent: coordinates the plan and compiles the final answer
- Research Agent: retrieval and knowledge gathering
- Memory Agent: project context, assumptions, continuity
- Reasoning Agent: advanced inference plus multimodal reasoning
- Quality Agent: testing, verification, consistency checks
- Tooling Agent: tool execution and integrations
This separation is what lets the system stay robust as capabilities expand. Each agent has a clear job, and the orchestrator keeps the overall task coherent.
2) Knowledge and retrieval that supports real research
The research assistant needs to cite and ground itself.
- Pinecone vector store for semantic retrieval
- StackExchange API for targeted technical knowledge extraction
- Lean documentation scraper for pulling authoritative references when formal reasoning gets specific
The goal is to reduce time lost to searching and keep responses anchored in retrievable sources.
3) Math and symbolic computing as first class tools
A core requirement for academic users is being able to execute formal and mathematical work.
- WolframClient for symbolic computation
- Lean plus Mathlib for theorem proving and formal verification
- SageMath, Coq, and MATLAB support for broader academic compute needs
This turns the assistant into a computational partner rather than only a writing helper.
4) Virtualization and execution environments
To run real workloads safely and repeatably, the system executes inside controlled environments:
- Dedicated VM or container per workspace
- Runs a guest OS (Windows, macOS, Linux) when needed
- Executes language runtimes and dependencies inside that environment
This supports messy real world repos and research tooling without forcing users to configure everything locally.
5) Browser automation for research plus action
Research often requires interacting with portals and UIs that are not API friendly.
- A Parallel Browser Hub for multi tab execution
- A Credential Vault for secure login flows
- A Deep Vision Layer to support spatial UI interaction when DOM automation is insufficient
6) Code execution and CI style reliability
For repo level work, the system includes:
- Repository Executor to run projects, not just read them
- Dynamic Debugging and Self Correction loops when execution fails
- S3 storage to persist outputs, updated repos, and artifacts
7) Monitoring, state estimation, and load management
Autonomous systems need resource awareness.
- Usage and performance metrics feed an Adaptive Load Manager
- The system can change strategies when cost or complexity spikes instead of blindly continuing
8) Security and interruptions
Autonomy without controls is a liability. The platform includes:
- Lambda Auth Handlers for secure integration access
- An Ephemeral Sandbox for risky execution contexts
- A broader stop and ask approach for sensitive actions such as credentials, authentication, and protected resources
How it works in practice
Flow A: Research, compute, write
- The user asks a research question or defines a goal.
- The orchestrator decomposes the work across retrieval, compute, and drafting.
- The Research Agent gathers sources and references.
- The system executes math or code as needed (Wolfram, MATLAB, Lean, Python).
- The Quality Agent validates outputs and flags inconsistencies.
- The assistant returns a grounded answer plus reusable artifacts.
Flow B: Run the repo, fix the failures
- The user provides a repository or project goal.
- The system sets up runtimes and dependencies in the dedicated environment.
- It executes the project.
- If it fails, it debugs, edits, and reruns until stable.
- Outputs and updated code are stored for handoff and iteration.
Flow C: Parallel browsing for literature and evidence
- The user requests multi source research.
- Parallel browser agents collect information simultaneously.
- Credentialed steps are gated and handled via the vault and auth handlers.
- Retrieved evidence is summarized and linked back into the project context.
Implementation snapshot
- Modular backend designed to support new tools and interpreters without destabilizing the core.
- Secure artifact storage through S3.
- First functional prototype delivered in roughly 4 months, followed by iterative expansion.
Expected impact
Chip Inc’s aim is to reduce time spent on repetitive research tasks and lower the barrier to advanced computation for academics, especially for users who do not want to become infrastructure engineers just to run serious workflows.
The bigger shift is qualitative: research time moves from setup and busywork to analysis and insight.
This project shows what it takes to make AI genuinely useful for complex knowledge work. The value is not a larger model. It is the engineering around the model: orchestration, execution, verification, retrieval, and safety controls.


